Running an agency isn’t just about creative campaigns and client strategy, it also means managing a complex web of financial responsibilities behind the scenes.
When it comes to marketing agency accounting, managing payroll and taxes is more complicated than you’d think!
Unlike many traditional businesses, marketing agencies often rely on a unique mix of full-time employees, part-time staff, remote workers, marketing freelancers and contractors, scattered across different states, or even countries.
This blend of talent makes payroll processing and tax compliance significantly more challenging. From handling different payment schedules to navigating multi-state tax laws and contractor classifications, there’s little room for error.
In this guide, we have a few practical tips to help agency owners and managers streamline their payroll processes, avoid costly tax mistakes, and stay compliant, no matter how diverse their team structure may be!
Managing payroll in a marketing agency is more complex for a number of reasons:
These factors mean that your setup must flex with headcount, locations, and project velocity while staying compliant.
So, how do you do that, exactly?
Here are some tips to help you streamline the process and stay on top:
Create a one page compensation policy that specifies salary bands by role, overtime eligibility, commission formulas tied to measurable outcomes, bonus timing, benefits, stipends, and what is or is not taxable.
Document what counts as remuneration for each role, so offers, promotions, and audits reference a single source of truth.
This means that you, your employees and any external auditors can be on the same page and everyone knows why things are the way they are.

Setting out a clear definition of the different classifications and correctly identifying who fits into each category makes a huge difference when it comes to managing your payroll and ensuring the correct documents are in order for tax purposes.
Record your classification rationale and review it annually.
Check out this video by Accounting Instruction for a quick explainer:
One new hire in a new state can trigger registration for payroll withholding, unemployment insurance, and possibly local city or county rules.
Maintain a living map of employee locations and register before the first paycheck. Do the same for international hires.
The cadence of payments can be adapted to suit your cash flow and budgeting requirements, as long as it is consistent and clearly set out.
For example, you can:
Consistency reduces disputes and simplifies accruals, making it easier to manage your agency’s payroll smoothly.
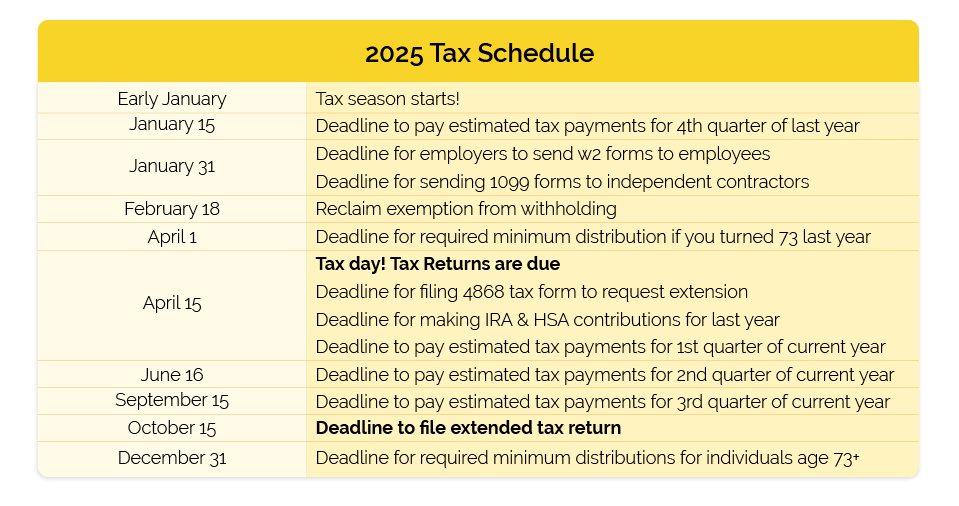
To cover the bases for compliance, you need to:
Getting these basics in place from the start makes a big difference down the line.
Every team member should see period dates, gross pay, hours and overtime if applicable, taxes, deductions, employer contributions, and year to date totals.
You can standardize your layout with a pay stub template, and if you are just starting out a free pay stub generator can help create readable statements while you implement a full payroll system.
Use truthful figures only and never fabricate income or deductions.
Clarify tax treatment item by item. Some perks are taxable, many reimbursements are not if they’re substantiated, and health or retirement contributions have specific coding rules.
Add one line per benefit in your policy that states whether it is taxable or not and how it flows through payroll.
Use written agreements that cover scope, IP, confidentiality, and governing law. Define currency, payment rails, and who bears FX fees.
Reassess status if work becomes ongoing and directed by your team.
Having a clearly set out agreement means both parties have clarity and there is no room for ambiguity or potential tax headaches.
Keep detailed records of hours worked, salaries, bonuses, tax forms (W-2s, 1099s), and benefit contributions.
Periodically audit payroll processes and tax filings to catch errors and maintain compliance.
Auditing your own records at intervals throughout the year means you can find and fix issues before they compound over time.
For example, an error that is repeated throughout one quarter is much easier to rectify than one that has repeated for a full year.

You can use a simple, four-week rollout plan to implement the changes needed to manage your payroll and taxes properly:
By following these steps, you can streamline your marketing agency accounting process and save yourself from many future tax and payroll headaches!
Great creative work rests on sturdy operations and effective accounting.
With thoughtful policies, correct classification, timely registrations, clean filings, and transparent pay communication, agencies can protect margins, elevate trust, and scale with confidence.
Using cloud-based payroll software automates calculations, tax withholdings, and direct deposits, saving time and reducing errors. It also helps with recordkeeping and compliance. If you are just starting out, you can use a pay stub generator tool to record the key information you need. Read the full guide for more tips to manage your agency’s payroll well.
Ensure accurate worker classification, file taxes on time, and use automated systems or services to calculate and remit payroll taxes correctly. Read the full guide for more tips to manage your marketing agency’s payroll and taxes.
Small to mid-sized agencies often benefit from outsourcing, as it reduces administrative burden, ensures compliance, and provides expert support, especially if internal resources are limited. Larger marketing agencies with the resources for full-time internal administrative staff need to look at the cost/benefits of outsourcing for their specific needs. Read the full guide for more tips to manage your marketing agency’s payroll.
Deel: 2025 Payroll Compliance Checklist and Tax Law Guide
Investopedia: Payroll Explained: Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Payroll Taxes